23rd May 2024
Guest Blog: Data-driven leadership development: transforming organizations through informed decisions

By Prof. Llewellyn E. van Zyl
Chief Solutions Architect, Mindset Management
Extraordinary Professor of Positive Psychology, Optentia Research Unit, North West University
This guest blog follows Prof. Llewellyn E. van Zyl’s talk on data-driven leadership during the latest Power Hour. Click here to watch the talk on demand.
—-
By embracing a data-driven approach to leadership development, organizations can bridge the gap between leadership behaviors and organizational performance metrics, thereby unlocking new pathways to success. In this article, we will explore the transformative potential of data-driven leadership development, from the importance of linking leadership behaviors to core organizational performance metrics to the practical steps organizations can take to harness the power of data in their leadership development initiatives.
It goes without saying that organizational success is largely dependent upon effective leadership. Multiple studies have shown that a staggering 70% of the variance in employee engagement can be attributed to leadership and how leaders manage their people. Effective and empowering leadership also serves as a defense against high staff turnover and helps buffer against the negative effects major organizational changes have on employee motivation and performance. It is therefore not surprising that organizations spend billions of dollars on an annual basis to provide leaders with the skills required to help elevate their organizations to higher levels of performance and profits!
Yet, despite its critical importance, many organizations continue to navigate their leadership development interventions without a compass by relying on intuition rather than empirical evidence to guide their strategies. This lack of data-driven decision-making not only undermines the efficacy of leadership development initiatives but also hampers organizational performance as a whole.
It’s a sobering reality: despite the plethora of leadership development programs and interventions being implemented, many organizations fail to establish a clear link between leadership behaviors and core performance metrics. Instead of leveraging real-time data to inform their strategies, they resort to generic ‘one-size-fits all’ approaches that rarely yields any tangible returns. As a result, many organizations are not able to show the true impact of their leadership development interventions on organizational success.
However, this status quo is neither inevitable nor insurmountable. By embracing a data-driven approach to leadership development, organizations can bridge the gap between leadership behaviors and organizational performance metrics, thereby unlocking new pathways to success. Through rigorous analysis and empirical research, organizations can identify the specific behaviors, competencies, abilities, attributes, and values that directly drives organizational outcomes, thus allowing them to tailor their leadership development efforts accordingly.
This shift towards data-driven leadership development represents a paradigmatic evolution in how organizations approach talent management and organizational effectiveness. By harnessing the power of data, organizations can align their leadership development strategies with the broader goals and objectives of the organization to ensure that every investment in leadership development yields tangible returns.
In this article, we will explore the transformative potential of data-driven leadership development, from the importance of linking leadership behaviors to core organizational performance metrics to the practical steps organizations can take to harness the power of data in their leadership development initiatives. By doing so, I hope to help organizations employ more data-driven approaches to their leadership development initiatives to not only help improve organizational performance but to improve the efficiency of their interventions.
Importance of Data in Leadership Development

Data serves as the cornerstone of effective leadership development initiatives as it provides a proverbial roadmap for which leadership characteristics lead to organizational growth and performance. Rather than relying on gut feelings or anecdotal evidence, organizations can leverage empirical data to inform their assessment and development strategies. Through data, organizations can identify the core competencies, leadership behaviors, abilities and mindsets that predict core organizational success factors. By understanding the attributes that directly predict performance, organizations can start to make informed decisions about their developmental interventions that are grounded in objective reality rather than subjective opinion or hot topics in the industry.
Moreover, data-driven approaches can not only show how leadership affects performance, but can help understand what highly effective leadership looks like in the environment in which the organization operates. By assessing others against this profile of highly effective leadership, the organization can get a more comprehensive understanding of the strengths, weaknesses, and developmental needs of their leaders. This precision allows for targeted interventions that address specific areas for improvement that can maximize the impact of leadership development efforts.
Data also plays a pivotal role in anticipating and addressing future organizational leadership needs. By analyzing current and projected business goals alongside existing leadership capabilities, organizations can identify gaps and implement targeted development initiatives. This proactive approach ensures that the organization is equipped with the right leadership talent to navigate future challenges.
Data also empowers organizations to create hyper-personalized development plans that are tailored to organizational growth goals and strategic priorities. As we know, effective leadership is not a one-size-fits-all proposition. It must be aligned with the unique goals, values, and objectives of the organization but also to the specific learning and development needs of the leader. By identifying the leadership behaviors and competencies that drive organizational success, organizations can ensure that their development initiatives are laser-focused on achieving tangible business outcomes. Further, these approaches also help in selecting relevant learning resources / approaches and content that are aligned to the specific needs of each individual and can help track progress in their leadership development journeys over time.
Furthermore, leadership development is not a once-off initiative, but an ongoing process that requires continuous evaluation and refinement. Data-driven approaches help to facilitate continuous improvement by providing real-time feedback on the effectiveness of leadership development initiatives. By tracking key performance indicators and monitoring progress over time, organizations can identify areas for adjustment and optimization, ensuring that their leadership development efforts remain agile and responsive to changing circumstances.
Given that leadership development represents a significant investment for organizations in terms of time, resources, and effort, data-driven approaches can help to maximize the return on this investment by ensuring that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently. By identifying the leadership behaviors and competencies that have the greatest impact on organizational performance, organizations can prioritize their development efforts and allocate resources where they will have the most significant impact.
Develop and Validate a Data-Driven Leadership Capability Model

The first step in developing effective leadership is that organizations must first understand what constitutes excellent leadership within their unique context. Highly performing organizations are increasingly turning to data-driven approaches to construct their Leadership Capability Profiles. A leadership capability profile is a structured framework that outlines the key competencies, experiences, abilities, and values required for effective leadership within a given organization. It serves as a roadmap for identifying, assessing, and developing leadership capability at various levels and provides a clear understanding of factors that contribute to leadership success. Data-driven leadership capability profiles are analytically driven and employ empirical data from diverse sources to create and validate more robust frameworks for leadership effectiveness that align leadership behaviors with organizational goals and objectives.
Constructing a robust data-driven leadership capability model requires a multifaceted approach that integrates a wide array of qualitative and quantitative data points from various sources. By gathering insights from leaders at different levels, organizations can identify the key attributes and behaviors associated with effective leadership. This approach involves several steps:
- Understand The Organizations’ Context. A participatory action research approach can be employed with executive leadership in order to explore the current organizational environment in which highly performing leaders’ function. Here, the focus is on understanding the nature of the business, its operational model, and its key challenges. A definition for leadership capability within this context is then co-constructed which highlights the capabilities required for formative functioning at each level of leadership within the business. Organizational values are discussed and their relationship to organizational performance metrics established.
- Identify and Analyze Highly Performing Leaders. Highly performing leaders should be identified and through structured interviews, job shadowing, evaluating key KPIs and reviews of past performance appraisals, the core capabilities they exhibit which make them highly effective should be identified. High-performing leaders serve as invaluable sources of knowledge, offering firsthand insights into the practices that drive success. By conducting interviews and observing their behaviors, organizations can distill these insights into a comprehensive capability model tailored to their specific context. Here the focus should be on identifying the core functional/behavioral competencies, past leadership experiences and cognitive abilities that they exhibit that make them different from other leaders in the organization. Past psychometric results on personality, work preferences, leadership styles and the like could also be reviewed. Furthermore, these leaders’ teams should be interviewed to determine what they do differently. Through thematic content analysis, one would be able to identify the main characteristics that lead to performance in the organization.
- Translate Organizational Values into Metrics. Next, organizational values should be evaluated and translated into measurable competencies. Organizational values define the culture, climate and contribution of leaders related to achieving the organization’s mission. Aligning the model with organizational values and growth goals ensures that it reflects the unique requirements of the organization. By accounting for contextual factors, organizations can ensure that their leadership development efforts are targeted and impactful.
- Construct and Validate the Capability Profile. Once all the data is collated, a draft leadership capability profile is constructed. This profile should cluster the required capabilities in terms of (a) leadership performance (competencies, leader experiences) and (b) leadership potential (abilities and values). This profile should then be transformed into a quantifiable metric and tested within a small sample of leaders in the organization. This can be done through techniques like 360-degree evaluations. The factorial validity of the profile should first be explored, and the reliability of the instrument established. Then the profile should be regressed on/linked to important (hard and soft) business unit and overall organizational performance metrics in order to ensure that these factors are indeed indicators of success within the organization. In other words, we need to ensure that these capabilities actually predict important performance metrics. The final step is to evaluate which factors are significant predictors of performers and which aren’t. Factors that are significant predictors of performance should stay in the profile, and factors which have no significant relationship removed.
- Finalize the Capability Model. Once this process has been completed, the capability model is finalized, and it should be workshopped with key stakeholders (e.g. Figure 1).
Once this data-driven capability profile has been developed and preliminarily validated, we are able to start building the roadmap on which our leadership development strategy will be based. Although we have constructed a leadership capability profile that is linked to important organizational metrics, we still need to assess our entire populus against the profile and determine how this affects our employees.
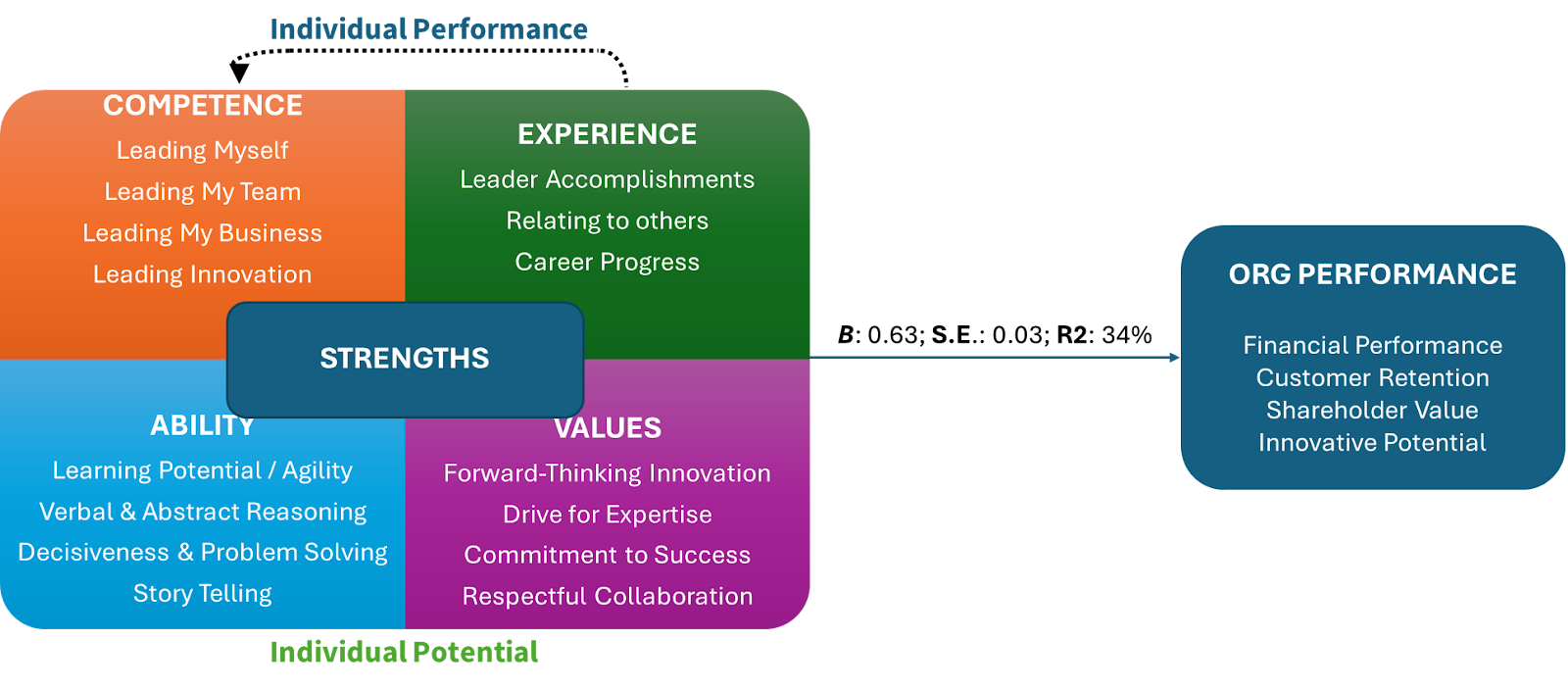
Figure 1. Example of a Data-Driven Capability Profile
Building a data-driven leadership development roadmap

The next step is to construct a predictive process model that links individual employees’ experiences to personal and organizational performance metrics, and then to determine to which extent the newly developed leadership capabilities influence the relationships between the factors. This will help target the exact leadership capabilities to develop first in order to improve employees’ performance. The job-demands and resources (JD-R) framework could provide a comprehensive evidence-based process model on which to build this developmental roadmap.
The JD-R framework is a widely used theoretical process model that explains the relationship between job characteristics (job demands and resources), employee well-being, and performance. According to this framework, job demands refer to aspects of the job that require sustained effort and energy, such as workload and time pressure, while job resources are the aspects that facilitate the achievement of work goals and reduce job demands’ associated costs, such as social support and autonomy. The JD-R framework posits that job demands can lead to strain and burnout, while job resources can promote motivation and engagement, ultimately influencing employee performance. Leadership capability serves as a crucial moderator in this relationship, as effective leadership can mitigate the negative impact of job demands, provide additional resources, and enhance employees’ capacity to cope with challenges, thereby positively influencing performance outcomes. By effectively leveraging leadership capability, organizations can optimize the balance between job demands and resources, fostering a work environment that promotes employee well-being and performance excellence.
To build a process model that is tailored to the unique environment of the organization, the following steps should be followed:
- Determine the most appropriate job demands (e.g. workload or time pressure) and job resources (e.g. employee voice or appreciative feedback), motivational factors (e.g. employee engagement), and key performance indicators (e.g. customer satisfaction) within the organization.
- Construct and disseminate a survey that measures these factors within the entire population. Ensure that enough demographic factors are included in order to link leaders to their teams.
- Assess leaders against the leadership capability profile. A multi-approach, multi-method strategy should be used whereby different facets of the capability profile are measured in different ways. This can include psychometric tests, simulations, and behavioral-based interviewing.
- Combine the datasets from Point 2 and Point 3.
- Test a structural (regression) model that links the job demands, resources and motivational factors to the performance metrics. Analyzing the data involves building structural path models that illuminate the relationships between different factors and outcomes. Regression and moderation techniques help identify the most significant drivers of success which enables organizations to prioritize their development efforts more effectively. Then determine how the leadership capability profile moderates or affects the relationship between job demands/resources and the motivational factors as well as how this directly relates to performance. This will afford you the opportunity to determine which employee-level factors are the main contributors to – or detractors from – performance as well as which leadership capabilities affect this relationship the most (e.g. Figure 2).
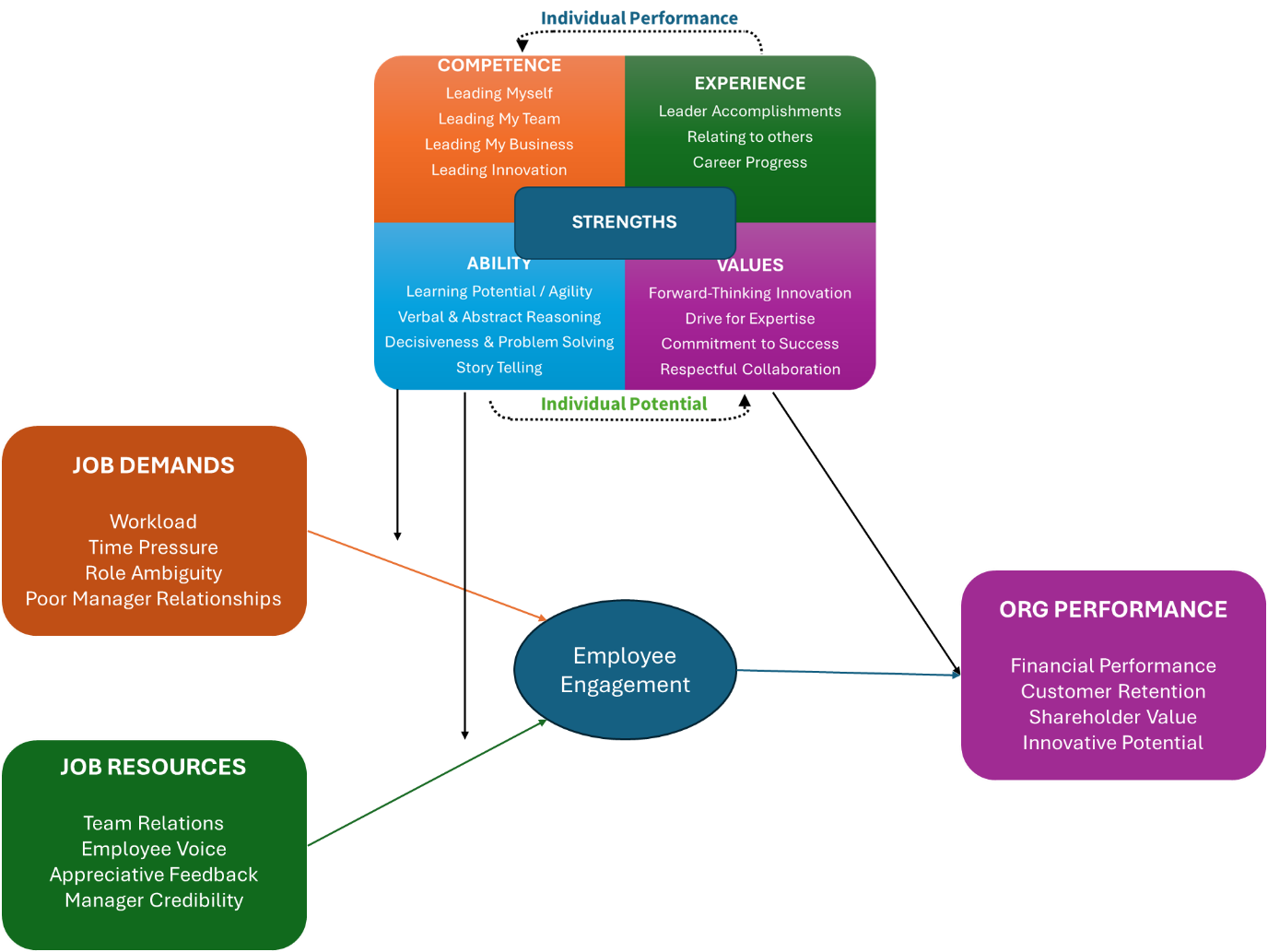
Figure 2. Structural Process Model of Job Demands, Resources, Leader Capability and Performance
Developing Customized Leadership Development Plans

Armed with insights from the validated leadership capability model and the structural process model, organizations can now develop personalized development plans and craft customized learning journeys for each individual leader. By identifying specific areas for improvement and designing targeted interventions, organizations can support leaders in not only reaching their full potential, but also ensuring that their developmental initiatives have a direct impact on the organization’s bottom line.
But how can we use the data to help inform the development of our hyper-personalized leadership development plans? Well, there are several ways in which this model can inform your developmental interventions:
- Firstly, organizations can utilize the data gathered from assessments to identify the core factors that are directly influenced by leaders’ capabilities. By analyzing this data, organizations can pinpoint the specific behaviors, competencies, and attributes that are most critical for success in each leadership role. This analysis serves as the foundation for designing customized learning journeys that target these key areas.
- Secondly, based on the assessment results, organizations can identify the specific development needs of each leader. This involves identifying their strengths and weaknesses, as well as areas where they may need additional support or skill development. For example, if a leader demonstrates strong strategic thinking skills but struggles with delegation, their learning journey may focus on delegation techniques and time management strategies.
- Thirdly, organizations can translate the identified development needs into practical learning strategies and interventions. This may include a combination of formal training programs, coaching sessions, mentoring relationships, experiential learning opportunities, and self-directed learning activities. Each component of the learning journey is carefully selected to address the individual needs and preferences of the leader, ensuring maximum impact and engagement.
- Fourthly, organizations can design learning journeys that incorporate a variety of resources and modalities to accommodate different learning styles and preferences. This may include traditional classroom-based training, e-learning modules, workshops, peer learning circles, and on-the-job learning experiences. By offering a diverse range of learning opportunities, organizations can cater to the diverse needs and preferences of their leaders and maximize the effectiveness of the learning journey.
- Finally, ongoing evaluation and feedback are essential components of the customized learning journey. By regularly assessing the progress of leaders and soliciting feedback on the effectiveness of the learning interventions, organizations can make adjustments as needed to ensure that the learning journey remains relevant and impactful. This iterative approach to learning and development allows organizations to continuously support the growth and development of their leaders, ultimately driving organizational success.
Conclusion
Data-driven leadership development represents a paradigm shift in how organizations approach talent management and nurture their leadership pipelines. By constructing robust, empirically validated leadership capability models aligned with organizational values and performance metrics, organizations can pinpoint the critical competencies, experiences, and attributes that distinguish high-performing leaders. Integrating these insights with theoretical frameworks can highlight the interplay between leadership capabilities, job demands, resources, and key outcomes, enabling you to design hyper-personalized development plans with real-world impact.





